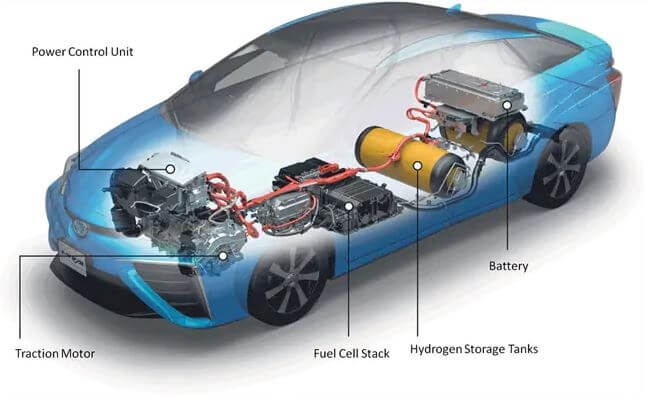
The use of hydrogen energy refers to the conversion of hydrogen into electricity, thermal energy, etc. Hydrogen is an energy that is obtained through natural gas, water electrolysis, solar photosynthesis and other forms. Unlike coal, oil and natural gas which can only be extracted from the soil.

The discovery of hydrogen is attributed to the British chemist and physicist Henry Cavendish (1731-1810). As early as the sixteenth century, however, the famous Paracelsus (1493-1541) stated that a gas is produced when iron filings and acid come into contact. In the seventeenth century the Flemish chemist and physician, Jean Baptiste van Helmont (1579-1644), was accidentally exposed to the said gas, but did not isolate or even collect it: The Irishman Robert Boyle (1627-91) instead collected the said gas by chance, but did not conduct research.
It was only known it was combustible, and nothing else. In 1700 the French pharmacist, Nicolas Lémery (1645-1715), mentioned it in his Report to the Academy of Sciences in Paris.
Cavendish was the first to collect and study hydrogen, but his understanding of hydrogen was not correct. He believed that water was an element and hydrogen was water with too much “phlogiston” (name given by chemists of the eighteenth century to a hypothetical substance that would be released from compounds by combustion or calcination, of which it would constitute the principle of flammability).
Only in 1782 did Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier (1743-94) clarify that water was not an element but a compound. In 1787 he called that flammable gas hydrogen, which means “water producer”, and confirmed it was an element.
As a fuel for internal combustion engines, hydrogen is a recent application. The use of hydrogen in internal combustion engines has a long history.
The first hydrogen-powered internal combustion engine in human history can be traced back to 1807, when French politician and inventor, naturalized Swiss, François Isaac de Rivaz (1752-1828) created a single-cylinder hydrogen internal combustion engine.
Due to the limited level of technology at the time, however, the production and use of hydrogen was much more complicated than using resources such as steam and gasoline. Therefore, hydrogen-powered internal combustion engines were overtaken by steam, diesel and gasoline engines.
During World War II, hydrogen was used for the propelling the V2 rocket. In 1960 liquid hydrogen was first used as a fuel for space-based power. In 1970 the ill-fated Apollo 13 spacecraft launched by the United States used liquid hydrogen for its rocket liftoff. Hydrogen has become a common fuel in the rocket industry. All this, from the V2 rocket onward, thanks to German scientist Werner von Braun (1912-77).
For modern space shuttles, it is more important to reduce fuel weight and increase payload. The energy density of hydrogen is very high, i.e. three times that of normal gasoline. This means that the space shuttle uses hydrogen as fuel and its weight can be reduced by 2/3 compared to a “full tank” of traditional fuel, which is undoubtedly extremely advantageous for spacecraft.
Scientists are studying a spacecraft with “solid hydrogen”. Solid hydrogen is used as both a structural material and energy fuel for the spacecraft.
A variety of fuel cell vehicles were publicly tested in the late 1980s and the possibility of replacing batteries with small fuel cells materialized in the late 1990s.
In the 21st century, faced with environmental pollution and other crises, hydrogen fuel cells are developing rapidly and ever more hydrogen-powered vehicles are starting to enter the market.
Hydrogen energy has become the subject of intense research in various countries and the new energy is stubbornly tackling the current difficult situation facing the planet. According to a survey by the U.S. Department of Energy, in recent years industrialized countries around the world have invested in the development of hydrogen energy, with a 20.5% annual increase of investment. The United States has always attached importance to hydrogen energy. In 2003 the Bush II Administration invested 1.7 billion US dollars to launch the hydrogen fuel development plan, and submitted key development projects such as industrial hydrogen energy production technology, storage technology, and direct application of hydrogen energy. In February 2004 the U.S. Department of Energy announced the “Action Plan for Research, Development and Testing of Hydrogen Energy Technologies.”
Hydrogen economic development in the United States has shifted from the systematic implementation phase to the evaluation and policy formulation phase. The first hydrogen station was established in the United States in May 2004: a third generation domestic energy station, i.e. a stationary hydrogen production device in California, started its trial phase.
In July 2005 Germany’s Daimler Chrysler (1998-2007), one of the first hydrogen fuel cell producing companies in the world, successfully developed the “fifth generation battery vehicle” in the United States by setting a trip data recorder for fuel cell vehicles in motor cars: a full travel distance of 5,245 kilometres at a top speed of 145 km/h.
Conversely, in China, the energy development strategy is focused on the strategic development of national economy because China’s fossil energy has shown it still has few recoverable reserves: coal amounts to 114.5 billion tons, oil to 3.8 billion tons and natural gas reserves to 1.37 trillion cubic meters, which account for 11.6%, 2.6% and 0.9% of world reserves, respectively.
China has a large population and insufficient per capita resources. Per capita recoverable coal reserves are only half the world average, and oil is only about one tenth. Per capita energy consumption is obviously lagging behind, as is transport energy recovery.
At the same time, car exhaust gases have become the most important factor in air pollution, particularly urban air pollution. The pursuit of new clean energy is thus of particular importance for China’s sustainable development.
During the recent Five-Year Plans, the Ministry of Science and Technology included research and development of fuel cell vehicles and related technologies in the National Construction Science and Technology Plan. In January 2002 the Chinese Academy of Sciences launched a major project of the Strategic Action Plan for Science and Technology Innovation. It focuses on high-power proton exchange membrane fuel cell engine and hydrogen energy technology.
The Institute of Chemical Physics and the Chinese Academy of Sciences mainly rely on the State High-Tech Development Plan (863 Program) – Major Project for Electric Vehicles – of the Ministry of Science and Technology. The research and development of 75KW and 150KW fuel cell engines and hydrogen power are advancing in the field of technology with independent intellectual property rights.
Such world-leading technology will help China enter the hydrogen energy era as soon as possible. In addition to fuel cell cars and buses, China has successfully developed a total of over 2,000 kilometres in experimental operations. This shows that China has the ability to develop hydrogen-powered fuel cell engines. When the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games and the 2010 World Expo in Shanghai were held, the first fuel cell cars were tested successfully.