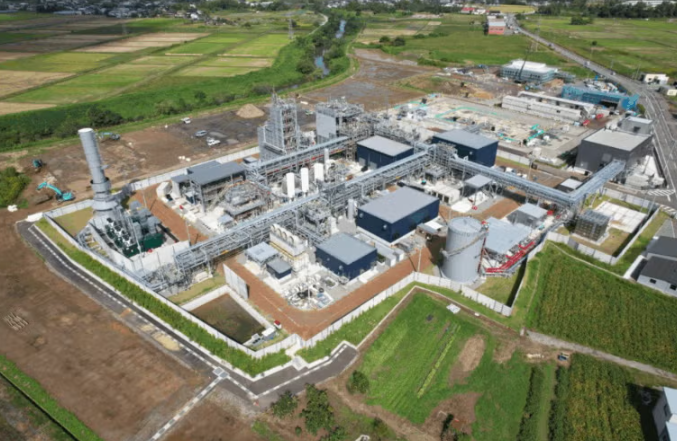
Bioethanol is increasingly recognized as a clean fuel alternative to gasoline and as a raw material for sustainable aviation fuel (SAF). However, moisture removal during the final dehydration stage is essential for fuel use, and this process traditionally consumes significant energy. MHI’s MMDS optimizes dehydration by replacing conventional methods with a molecular sieve separation approach. This enables high-efficiency production while cutting energy use by over 30%, reducing operational costs and ensuring stable output. The liquid-phase separation also allows a more compact equipment design.
“Achieving high ethanol purity at our pilot plant demonstrates that MMDS can deliver efficient, cost-effective, and compact bioethanol production,” said an MHI spokesperson.
Based on successful element tests at the pilot plant, MHI plans to accelerate development toward a demonstration plant to enable an early commercial launch. The company aims to advance high-efficiency manufacturing processes for hydrogen-free bioethanol, a clean fuel derived from plants, contributing to broader decarbonization efforts.
Through MMDS, MHI seeks to establish sustainable production methods that support carbon neutrality and offer a scalable solution for bioethanol and SAF production. The technology’s energy-efficient design addresses both environmental and economic challenges, providing a pathway for cleaner fuel adoption in transportation and aviation sectors.
MHI’s efforts reflect its commitment to carbon neutrality and sustainable industrial practices. By integrating innovative membrane technology into ethanol production, the company is setting a benchmark for efficient, low-emission fuel manufacturing. The upcoming demonstration plant will serve as a model for large-scale deployment, highlighting the feasibility of combining high purity, reduced energy consumption, and compact plant design in bioethanol production.
MHI continues to focus on decarbonization technologies and clean energy solutions. The success of MMDS underscores the potential for advanced manufacturing processes to transform bioethanol into a practical, sustainable energy source while contributing to global efforts for a low-carbon future. The company plans to leverage lessons from the pilot plant to refine operations and accelerate the transition to commercial-scale, environmentally responsible ethanol production.