While still in its infancy, power-to-gas provides a promising approach to convert renewable power into “green” hydrogen and methane, furnishing the renewables sector with a potentially lucrative array of end-uses. A newly announced set of dramatically larger and ambitious projects indicate it has made serious inroads within the energy transition.
Power-to-gas (sometimes abbreviated P2G or PtG) describes the process of converting renewable energy to gaseous energy carriers such as hydrogen or methane via water electrolysis—mainly alkaline electrolysis, proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysis, and solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOECs). In its most basic sense, the electrochemical process (see sidebar “Electrolyzer Technologies”) splits water into hydrogen and oxygen, and to convert it into methane, the hydrogen is reacted with carbon dioxide in the presence of bio-catalysts. The produced “green” hydrogen can be used in a range of pathways that promise to decouple renewable generation from electricity demand—helping to avoid surplus curtailment and potentially providing the sector with an assortment of new revenue streams (Figure 1).
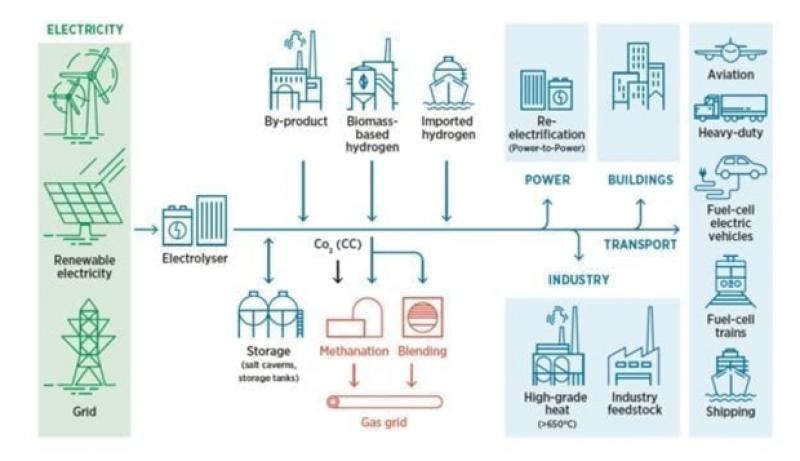
1. Power-to-gas essentially entails using an electrolyzer to split water into oxygen and hydrogen. The hydrogen can be used directly or fed into an assortment of processes. Courtesy: International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) Electrolyzer Technologies
Interest in electrolytic hydrogen has ramped up of late, owing to solar PV and wind’s declining costs and widespread uptake, and larger projects have been installed over the last five years. According to the International Energy Agency’s (IEA’s) June 2019–released “The Future of Hydrogen” report, three main electrolyzer technologies exist today: alkaline electrolysis, proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysis, and solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOECs).
Alkaline electrolysis. Introduced in the 1920s, this technology, which uses an aqueous alkaline electrolyte, has been in use for decades, mainly for hydrogen production in the fertilizer and chlorine industries. While it has a conversion efficiency that tangoes between 65% and 70%, it generally has the lowest investment cost and is considered robust, but challenges remain in dynamic modes, because efficiency and hydrogen quality may be severely affected in partial load operation. It also needs a larger plant footprint compared to other options.
PEM electrolyzers. Commercialized in the 1960s by General Electric, PEMs use a polymer electrolyte membrane and pure water as an electrolyte solution, which avoids the recovery and recycling of the potassium hydroxide electrolyte solution that is necessary with alkaline electrolyzers. Because its efficiency is higher than alkaline electrolysis—from 65% to 83%—and because these units are compact, better suited to dynamic operations, and respond quicker to load changes, a number of demonstrations have chosen this technology. Its drawback, however, is that PEMs need expensive electrode catalysts (platinum and iridium) and membrane materials, and their lifetime is currently shorter than that of alkaline electrolyzers.
SOECs. The least developed electrolysis technology of the three, SOECs have not yet been commercialized, though efforts are underway to bring them to market. They use ceramics as the electrolyte and have low material costs. But because they use steam for high-temperature electrolysis, they need a heat source, which is why experts suggest SOECs could thrive at nuclear, solar thermal, and geothermal projects. Another benefit is that SOECs can be operated in reverse mode as a fuel cell, converting hydrogen back into electricity.
The produced hydrogen, for example, can be used as a fuel—either for transport, displacing oil in light vehicles, railways, and marine applications—or as a feedstock for industry. In another prominently lauded application, it can be stored and reused as a fuel to generate power through gas turbines or fuel cells—and in an advantage over current battery storage, it can store larger quantities of power over longer time periods.
But, it could also be injected into the natural gas grid, albeit with certain limits, because too high a hydrogen content raises technical and safety issues. The UK, for example, only allows injection of 0.1% hydrogen by volume, while in parts of the Netherlands the limit is 12%. Advancements to loosen these constraints are underway, however. In November 2018, for example, a UK project led by HyDeploy—a partnership that involves Northern Gas Networks, Progressive Energy, and electrolyzer-provider ITM Power—began a year-long trial to explore injection of up to 20% of green hydrogen into a small gas network.
And, if converted to synthetic methane, the gas can be used as a direct replacement for fossil natural gas in gas networks, or as seasonal energy storage. That’s important because, as the UK-based Oxford Institute of Energy Studies notes in an October 2018 paper, P2G can introduce considerable flexibility into the energy system, resulting in “system coupling”—a closer integration between the gas and electricity system that could be more cost-efficient than full electrification of gas-fueled sectors.
The Many Avatars of Power-to-Gas
According to Martin Therma, F. Bauer, and M. Sterner, experts from Technical University of Applied Sciences (OTH) in Regensburg, Germany, who recently reviewed the world’s existing P2G hydrogen and methane projects, about 143 P2G projects have operated since 1988 in 22 countries. Only 56 hydrogen and 38 methanation projects were active in 2019. While the existing fleet mostly comprises pilot or demonstration projects under 1 MW, nearly 45% of these projects fed or planned to feed gas into the grid or reconvert it into power or heat.
The bulk of projects to date—64—were installed in Germany, followed by Denmark, the UK, France, the U.S., Switzerland, Spain, Canada, and Japan. Location is important because the choice of “process pathway” typically hinges on requirements of the “embedding energy system, such as hydrogen-tolerance of gas networks, gas buffering, mobility, [and] heat applications,”






