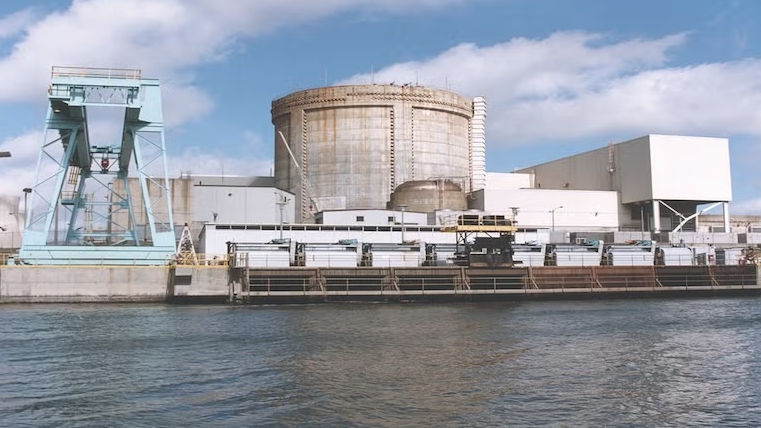
Unit 3 of the Crystal River nuclear power plant is on an accelerated decommissioning programme
Unit 3 at the Crystal River nuclear power plant in Florida, USA, saw the first use of an optimised segmentation process that was deployed as a method for accelerated decommissioning. This innovative approach for dismantling nuclear reactors was developed by Orano Decommissioning Services and is designed to reduce the volume of waste for disposal, as well as the amount of segmentation work required on reactor structures. The goal is to reduce both the time required and the cost of decommissioning.
Located in Citrus County, Florida, USA, Unit 3 of the Crystal River nuclear power plant was a Babcock and Wilcox 860 MWe Pressurised Water Reactor (PWR). Commissioned in 1976 the plant operated for 33 years until it was permanently shut down by owner Duke Energy in 2013. In October 2020, Accelerated Decommissioning Partners (a joint venture between Orano Decommissioning Services and demolition company NorthStar Group Services) completed a transaction with Duke Energy to begin decontamination and dismantling of the plant nearly 50 years sooner than had been originally planned. Accelerated Decommissioning Partners (ADP) thus became the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) licensed operator responsible for decommissioning the plant and also acquired the used nuclear fuel and the Independent Spent Fuel Storage Installation (ISFSI) assets.
Cutting decommissioning and disposal costs
The main drivers in the cost and schedule of a reactor decontamination and decommissioning operation are typically the extent of segmentation work to be performed on the reactor components. This is necessary to reduce their size so they can be removed and packaged for storage, shipment, and disposal. Another key cost driver is the number, size, and classification of the waste packages generated by the dismantling process.
The most contaminated and activated components of a nuclear energy reactor are concentrated inside the reactor pressure vessel (RPV) and the reactor vessel internal (RVI) structures. Dismantling the RPV and RVI structures generates the waste with the highest classifications when compared to the rest of the radioactive waste generated during reactor dismantling, with components classified as Class B, C, and Greater-than-Class C (GTCC), generating the highest cost for packaging, transportation, and ultimately their disposal.
Optimising cost therefore involves being able to segregate and distribute the generated waste within the various classifications to minimise the volumes of the costliest and most radioactive portion of the waste, GTCC and Classes B and C. This consideration is balanced against the operational costs needed to achieve the desired segmentation plan and involves finding the ideal compromise working within the following constraints:
Capabilities and limitations of the segmentation technologies available to efficiently and safely perform the separation and size reduction of highly radioactive reactor components.
Operational costs, since the segmentation work is labour-intensive and time-consuming due to the complex environment in which the segmentation equipment is used and the highly radioactive nature of the components to be segmented.
Capacities in weight and volume of the existing packaging systems licensed to receive and store and/or transport the generated waste in each category, driving the maximum size of the segments generated in each category. The high cost of procuring, transporting, and disposal or storage of the waste containers encourages achieving the highest packaging efficiency, which drives decisions towards more extensive segmentation of the reactor components.
The optimal segmentation strategy is driven by the goal to minimise the extent of the workplan engineering, on-site segmentation work, and the number of waste packages and shipments that typically come with the standard Full Segmentation strategy. One radical alternative to full segmentation is the “one piece” reactor removal approach, where the entire reactor vessel is shipped, including some of the reactor vessel internals. This solution has been successfully implemented in previous projects but involves very large packages and conveyance systems, which will be constrained by the limitations of the available transportation route infrastructure.
A compromise between the ‘full segmentation’ and ‘one piece’ strategies resolves these challenges by accommodating the transportation logistics restrictions with custom-designed waste containers large enough to substantially reduce the reactor component size reduction effort, while remaining transportable within existing road and transportation infrastructure capabilities.
Segmentation at Crystal River 3
By modelling the operating history of the reactor and how the various components had been irradiated and activated it was possible to predict the expected waste classification of each part of the Crystal River 3 reactor vessel and and its structures. The GTCC components are found in the core region of the internals and consist of the core barrel and baffle assembly, the surveillance capsule holders, surveillance capsule dosimeters, and in-core instrumentation detectors. These components have to be separated and segregated from the rest of the components so they can be packaged in containers that are stored onsite within the existing ISFSI until a final repository is available. Class B and C components are located in the other areas closest to the core region and consist of the control rod guide tube assemblies, upper core grid, the thermal shield, and lower internals assembly. Class A components include the plenum cover, plenum cylinder, core support shield assembly, reactor vessel, and vessel head.
As a first step in the process the reactor internals were segmented, extracted, and separated into two categories:
GTCC waste to be handled, packaged, and stored using conventional methods, such as Orano’s NUHOMS® interim dry storage systems
Contaminated and activated LLW internal structures
The internals were removed from the RPV, and precisely segmented underwater using remotely operated mechanical tools to segregate the GTCC components.
The emptied reactor vessel was then repacked using a tightly engineered placement based on each piece’s characterisation, with the highest activity components concentrated in the middle of the vessel. Less active low-level category waste was placed in the bottom and top sections. The reactor vessel and the repackaged internals were then immobilised in a specifically designed and qualified low-density cellular concrete mix to form the monolith, fixing the internals and providing radiation shielding.
The solid, grout-filled reactor vessel packed with waste was subsequently segmented into large sections with diamond wire saws and consistent with the internal waste materials distribution.
Outcomes of the optimised segmentation programme
The optimised segmentation and packaging strategy reduces the number of containers needed to receive the reactor vessel and vessel internals segments to a total of six. In contrast, a traditional reactor vessel dismantlement can generate up to 80 transport packages.
With optimised distribution of the activity within the monolith, the highest activity can be concentrated in one section and packaged into one Class B/C transportation and disposal package. The rest of the sections can be packaged into Class A packages. Two Rad Waste Canisters receive and store the GTCC portion of the reactor waste in the ISFSI. One Type B custom package is designed and licensed by the NRC to receive the middle section. One IP-2 metal container receives the top section, and two custom-designed and manufactured IP-2 supersacks receive the reactor head and bottom section.
Reactor dismantling operations at Crystal River 3 started in 2021. Components of the reactor cooling system including steam generators, main coolant pumps and motors, the pressuriser, and large bore piping were removed from the containment building and had been shipped off site for disposal by the end of October 2021. Segmentation of the reactor internals was conducted in 2022. Segregation, packaging, and on-site dry storage of the GTCC waste was completed in March 2023 while consolidation of the remaining internal structures into the vessel and grouting in preparation for final segmentation was concluded by the end of June 2023. Segmentation of the monolith was completed in October 2023.
Each section was packaged and shipped individually in a tailor-made container designed to transport and dispose of the waste in compliance with relevant regulations such as those of the NRC for Type B shipments and DOT for Industrial Packages, as well as the disposal site’s Waste Acceptance Criteria. All reactor segments were packaged and stored on site prior to off-site shipment to the Waste Control Specialists (WCS) disposal site in Andrews, Texas, in early 2024. A route survey determined that a combination of barge and road transportation offered the opportunity to ship packages as large as 16 feet (4.9m) high, 20 feet (6m) wide, and with a load of up to 450,000 kg, without road infrastructure modifications. This envelope formed the basis of the Optimized Segmentation strategy that was ultimately implemented.
Of the three segmented reactor vessel sections, only the middle section required an NRC-approved Type B package and an NRC Special Package shipping authorisation for this section was issued in August 2023. The two remaining reactor vessel segments – the bottom and top sections – only required shipping containers to comply with the DOT Industrial Package regulations (49 CFR 173).
Operations within the reactor building at Crystal River unit 3 were completed with the cleanup of the reactor cavity and the demobilisation of all equipment and staff from the reactor building by the end of October 2023, three years after the start of the project.
The optimised packaging plan and large container strategy significantly reduced the amount of segmentation work performed on the reactor structures and accelerated progress towards their removal from the containment building.