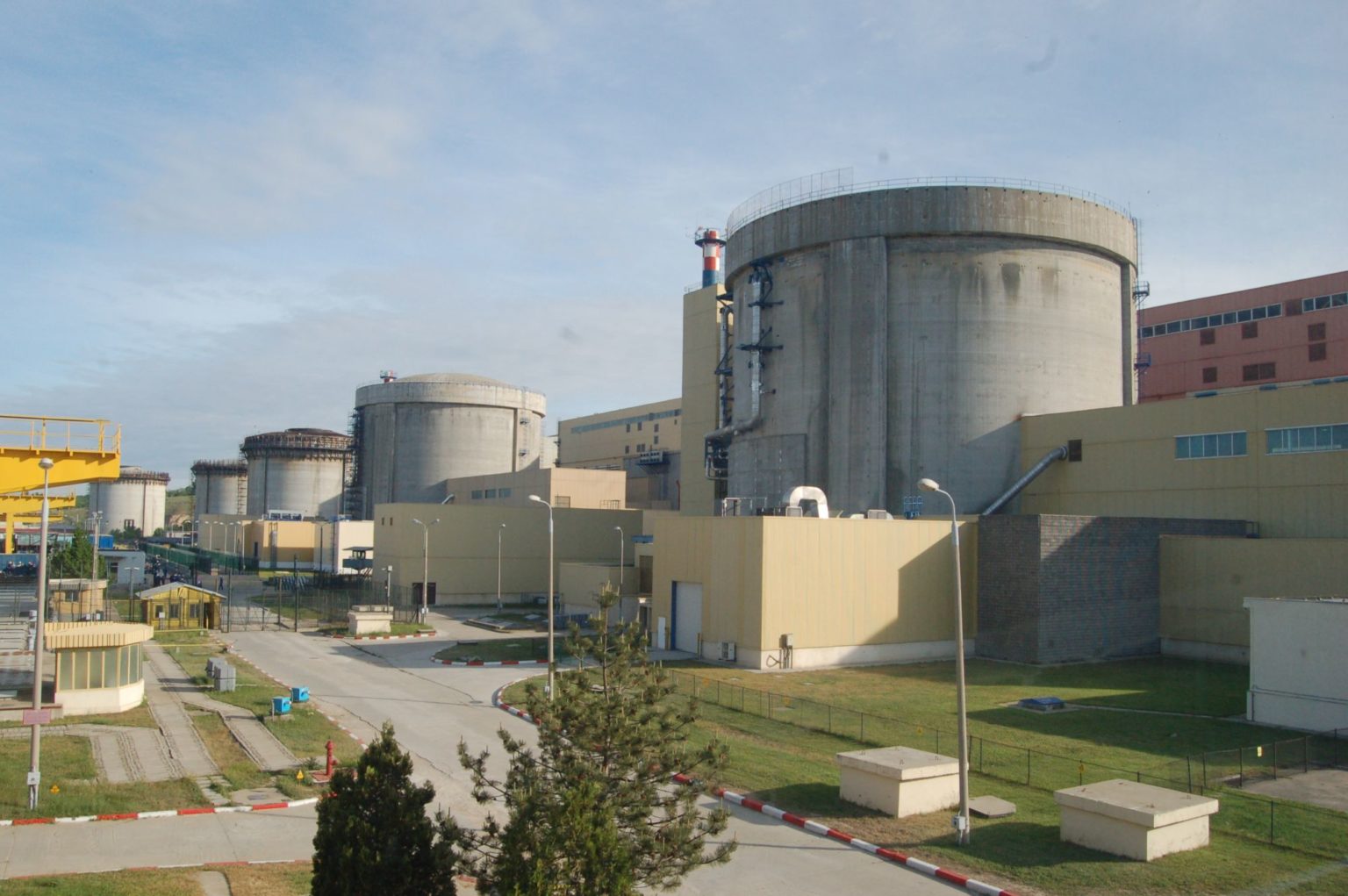
Kori unit 1
Kori Unit 1, a 576 MWe pressurized water reactor, began commercial operations in 1978. In August 2015, Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power (KHNP) withdrew its application to extend the reactor’s operating license, opting instead to apply for decommissioning in June 2016. The NSSC approved the permanent shutdown in 2017, requiring KHNP to submit a decommissioning plan within five years. KHNP submitted the plan in May 2021.
Following a thorough review, the NSSC confirmed that the decommissioning plan for Kori Unit 1 meets the technical standards of the Nuclear Safety Act. The evaluation included assessments by the Korea Institute of Nuclear Safety and the Nuclear Safety Expert Committee. NSSC Chairman Choi Won-ho stated: “Considering that Gori unit 1 is the first nuclear power plant decommissioning case in Korea, we conducted a detailed review of all evaluation items. We will closely inspect the decommissioning process to ensure that the public can feel safe even during decommissioning, and we plan to transparently disclose the inspection results.”
KHNP announced that full-scale decommissioning will begin following the approval. The process will start with dismantling facilities in the turbine building next month, followed by transferring used nuclear fuel to an on-site dry storage facility by 2031. The dismantling of the radioactive system and completion of the project are scheduled for 2037. KHNP CEO Hwang Joo-ho remarked: “The decommissioning of Kori unit 1 will be a turning point for internalising domestic decommissioning technology, fostering specialised personnel, and creating an industrial ecosystem beyond the simple demolition of equipment. We will transparently disclose the project process to the public and push forward the decommissioning project based on trust with the local community.”
In September 2017, the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute partnered with domestic companies, including Kepco Plant Service & Engineering and Doosan, to develop technologies for Kori 1’s decommissioning. These efforts focus on dismantling facilities, measuring land contamination, and advancing simulation, chemical decontamination, and waste disposal processes.
This milestone marks a significant step in South Korea’s efforts to safely manage nuclear reactor decommissioning while fostering innovation and community trust.