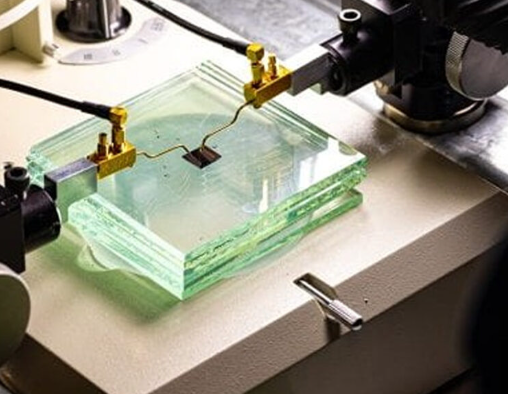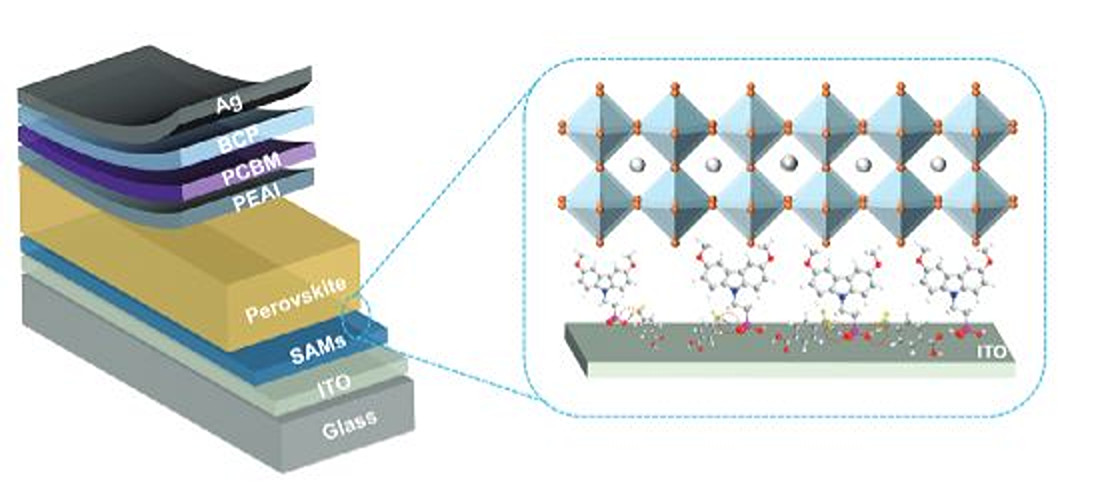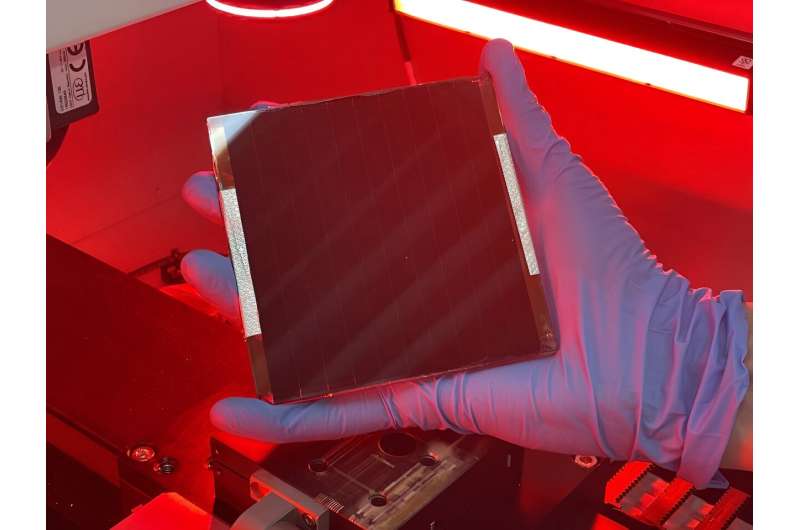
Borrowing from cell membranes, the protective barriers around cells in all living organisms, Penn State scientists have developed a new, cost-effective method for creating bio-inspired solar devices that could improve the performance of next-generation solar technology.
The researchers combined perovskite solar cell material—named for their unique crystalline structure that excels at absorbing visible light—with a synthesized version of natural lipid biomolecules to help protect against moisture-induced degradation. These biomolecules are fatty or waxy materials produced by our bodies don't dissolve in water, like cholesterol, and are a major component of cell membranes.
The biomolecules formed a membrane-like layer around the perovskite, boosting stability and efficiency in tests. The approach may have a transformative impact on how perovskite solar cells are designed, the scientists reported in the journal Advanced Energy Materials.
"Lipid molecules are naturally very good against moisture and cannot dissolve in water," said Yuchen Hou, who conducted this research while a doctoral student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Penn State. "We take a molecule that's evolved for many millions of years in nature with specific functions, and we see if the material can have the same function in our artificial device."
Perovskites are a promising solar cell technology because they exceed the efficiency of traditional silicon, according to Hou. But the material quickly degrades when exposed to moisture—like humidity in the air—and prior attempts to create protective layers have meant sacrificing efficiency and increasing costs, the scientists said.
With the new method, the biomolecules formed a nano-thin layer around the perovskite, protecting it from the elements and improving its lifespan. According to Hou, the method is cheaper and easier than conventional fabrication methods for silicon solar cells and still results in a material with good electrical properties, allowing them to make large devices without sacrificing efficiency or how much sunlight the cells can convert to electricity.
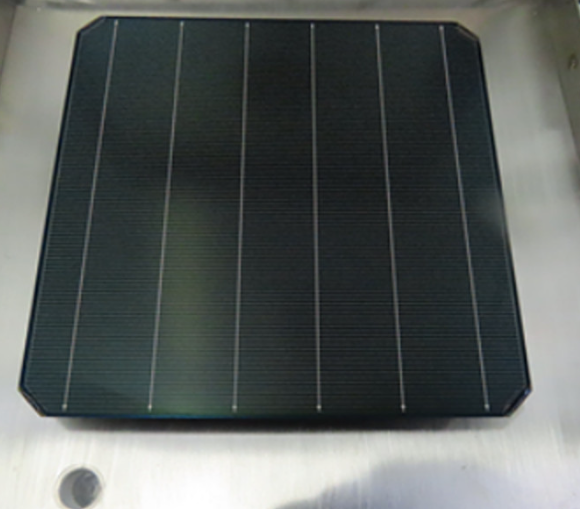
"In this work we are trying to solve two major problems in the field of perovskite solar cells—efficiency and stability," said Luyao Zheng, a postdoctoral scholar in the Department of Material Science and Engineering at Penn State and co-author on the study. "I think the major achievement here is that we were able to make a very large module with really good uniformity across the large area, and we've also been able to maintain a very good efficiency as well as stability."
A typical process for making perovskites involves wet chemistry—precursors, or ingredients, are liquefied in a solvent solution and then solidified into thin films. This material is then stacked with other layers to create a solar cell.
Adding the fatty biomaterial to the liquid perovskite precursors created an emulsion—the materials separated like oil and water but remained evenly dispersed across one another. This dynamic allowed the biomaterials to form a thin layer around the outside the perovskite, creating a bilayer structure.
"By directly depositing this micro-emulsion ink in a one-step process, we observed a self-assembly process where the top layer consists of nanoparticles wrapped by a biomolecular membrane," said Kai Wang, assistant research professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and a co-author on the study. "We anticipate this new bilayer concept will open pathways for including bio-inspired molecules in improving solar cell technology."
Using modeling techniques, the scientists found the interface also improved the electronic properties of the material and decreased surface defects that limit the efficiency of perovskite.
The researchers created 10-square-inch solar cells and field tested them in Pennsylvania from October through February. The devices showed consistent efficiency of more than 19% for more than 116 days of continuous use in natural weather conditions, including snow and humidity. This is comparable to the efficiency of commercial silicon solar cells, which is often between 15% to 20%, but the researchers said that their fabrication approach is simpler and cheaper than commercial processes.
"Typically, when you increase the module area, the efficiency of the solar cell decreases very quickly—you see a very sharp drop," Zheng said. "But in this work, when we upscale the module, we didn't see much decrease. I think that's a highlight of our work."
The process may be a good candidate for commercialization, the scientists said. Adding biomaterials would not significantly increase manufacturing costs—only a small amount of material is needed, and it is inexpensive. In addition, biomaterials are relatively environmentally friendly.
"When we talk about additives, they are often adding very small nano-metal materials that have some concerns about being toxic or hard to remove from nature," Hou said. "But this material is totally natural molecules. It will not damage the environment and it can easily decompose in nature."
The researchers said additional work will involve creating larger solar devices and conducting a systematic investigation of other biomolecules that could have similar beneficial properties.
"We have a lot of things to learn still to learn from nature," Hou said. "Natural materials and natural structures still can give us lots of inspiration during the creation of artificial material devices. I think this work is an example of how we can learn from nature to bolster our artificial devices."